Medical software development is a discipline that tolerates no shortcuts. Privacy regulations, system integrations, and patient safety leave little room for error.
The good news is that building reliable healthcare software in 2026 is entirely achievable. With mature cloud platforms, clearer compliance standards, and proven development practices, teams can deliver secure and effective solutions.
This guide explains the essentials of medical software development how to plan, build, and maintain compliant healthcare applications. It focuses on practical challenges, proven approaches, and current trends, without unnecessary jargon or hype.
What Is Medical Software Development?
Medical software development is the process of building digital systems used by healthcare providers, patients, and medical organizations. These systems include everything from appointment and billing platforms to clinical decision tools and medical imaging software.
What makes medical software different is the level of responsibility involved. It must be reliable, secure, and accurate by design. On top of that, it has to meet strict regulatory requirements such as HIPAA, GDPR, and other regional healthcare standards.
In short, medical software development is not just about shipping features. It’s about building software that people’s health and sometimes their lives depend on.
Types of Medical Software in 2026
Medical software spans multiple categories, each designed to solve a specific clinical or operational challenge. In 2026, these are the most widely used types across modern healthcare systems.
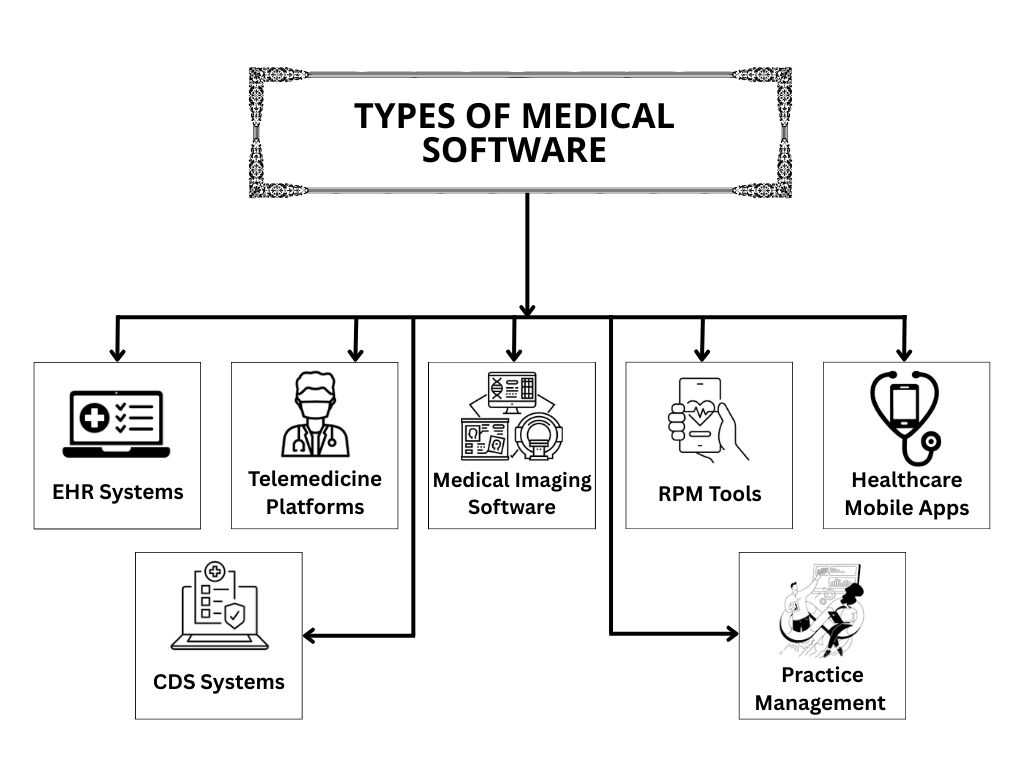
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Systems
EHR systems act as the central hub for patient information in hospitals and clinics. They store medical histories, prescriptions, lab results, and clinical documentation while integrating with telemedicine, imaging, and analytics platforms to support coordinated care.
Telemedicine Platforms
Telemedicine software enables secure remote consultations between patients and healthcare providers. These platforms support video visits, e-prescriptions, and follow-ups, with native integration into EHRs and connected health devices becoming the norm.
Medical Imaging Software
Medical imaging software processes and analyzes diagnostic images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. AI-assisted detection improves diagnostic accuracy and speed, while tight EHR integration streamlines workflows for radiologists and clinicians.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Tools
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) tools collect real-time health data from patients outside traditional care settings. By tracking vitals and sending automated alerts, they help clinicians manage chronic conditions and reduce avoidable hospital visits.
Healthcare Mobile Apps
Healthcare mobile apps focus on patient engagement and self-management. They commonly offer medication reminders, symptom tracking, and secure communication, with personalization and data security as top priorities in 2026.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) platforms support clinicians with evidence-based insights during diagnosis and treatment. They analyze patient data against clinical guidelines, helping reduce errors while improving consistency and care quality.
Practice Management Software
Practice management software handles scheduling, billing, insurance claims, and reporting. Deep integration with EHRs and telehealth systems minimizes administrative overhead and improves operational efficiency for healthcare providers.
Key Stages of Medical Software Development
Medical software development is a structured process with little room for shortcuts. In 2026, successful teams follow these stages to reduce risk and deliver compliant, reliable products.
Stage 1: Discovery and Requirements
This stage defines the problem and the users you’re building for. Teams work closely with clinicians, administrators, and compliance experts to identify core needs, workflows, and regulatory constraints. Clear requirements prevent costly rework later.
Stage 2: Planning and Prototyping
Here, ideas turn into workflows, wireframes, and early designs. Prototypes are tested with real users to validate usability and logic. Early feedback helps catch flaws before development begins.
Stage 3: Development
Developers build features, integrations, and data pipelines. Security, performance, and data accuracy are treated as first-class requirements. Iterative reviews with stakeholders are common at this stage.
Stage 4: Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing covers functionality, usability, security, and compliance. Automated tests ensure consistency, while manual testing uncovers real-world issues. This stage protects both patients and providers.
Stage 5: Compliance and Certification
Software is reviewed against legal and regulatory standards. This may include HIPAA, FDA, MDR, or regional certifications. Compliance is validated continuously, not just at release.
Stage 6: Deployment and Rollout
The system is released to production using phased or controlled rollouts. User onboarding and support processes are critical. Stability matters more than speed.
Stage 7: Maintenance and Continuous Improvement
Post-launch work never stops. Teams release updates, fix vulnerabilities, and adapt to regulatory changes. Reliability and uptime remain top priorities.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Healthcare software is built in one of the most regulated environments in the world. In 2026, compliance is not optional or secondary; it directly shapes system architecture, data flows, and operational processes.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA defines how patient health information must be protected in the US. Software is required to maintain the strict confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. Encryption, role-based access, and comprehensive audit trails are essential controls.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR applies to any software handling personal data of EU residents. It gives patients full control over how their data is collected, used, and deleted. Clear consent mechanisms and rapid breach reporting are mandatory.
FDA Approval (US)
Medical software classified as a medical device must undergo FDA review. This process requires detailed validation, documentation, and risk assessments. Approval timelines often span months and must be planned early.
ISO 13485 and ISO 27001
ISO 13485 focuses on quality management systems for medical software and devices. ISO 27001 governs information security management practices. Both standards are increasingly expected by healthcare partners and enterprises.
Regional Healthcare Regulations
Healthcare regulations vary by country and region. Examples include the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and Canada’s PIPEDA. Early regulatory research reduces compliance risks and delays.
Must-Have Features in Modern Medical Software
Modern medical software is judged less by features and more by reliability, security, and usability. The following capabilities are considered baseline expectations, not differentiators in 2026:
Secure User Authentication
Modern medical software relies on strong authentication by default. Multi-factor authentication and single sign-on are standard in clinical environments. Security starts at login, not after deployment.
Role-Based Access Control
Different users require different levels of access. Role-based permissions ensure clinicians, staff, and administrators only see what they need. This minimizes risk while supporting efficient workflows.
Interoperability with Other Systems
Medical software must integrate with EHRs, labs, pharmacies, and insurers. APIs built on HL7 and FHIR standards enable reliable data exchange. Interoperability directly impacts care quality.
Audit Trails and Logging
Every action within the system must be traceable. Audit logs support compliance, incident reviews, and accountability. They are essential in regulated healthcare environments.
Data Encryption (In Transit and At Rest)
Sensitive health data must be encrypted in transit and at rest. End-to-end encryption is now the norm. Strong security controls reduce breach risk and protect patient trust.
Intuitive User Interface
Healthcare professionals operate under constant pressure. Interfaces must be fast, clear, and easy to navigate. Good UX improves adoption and reduces training overhead.
Mobile Compatibility
Access from mobile devices is expected. Responsive design and native apps support clinicians and patients on the move. Mobile access improves engagement and responsiveness.
Biggest Challenges in Medical Software Development (2026)
Building medical software comes with constraints that don’t exist in most industries. In 2026, these are the challenges teams face most often:
- Constant regulatory changes: Healthcare laws and standards evolve frequently, requiring ongoing compliance monitoring, documentation updates, and staff training to avoid legal and trust-related risks.
- Complex system integrations: Legacy infrastructure and inconsistent data formats make integrating with EHRs, labs, and insurers time-consuming and unpredictable, even with modern APIs.
- High data security risks: Healthcare data is a prime target for attackers, making strong security architecture, audits, and access controls essential to prevent costly breaches.
- User adoption and training: Busy clinicians have little tolerance for friction, so poor UX, weak onboarding, or slow support can lead to low adoption and wasted investment.
- Scalability and performance: Growing user bases, data volumes, and integrations demand systems that scale reliably from day one, not as a post-launch fix.
Costs of Medical Software Development in 2026
Let’s talk numbers. Medical software is a serious investment, and costs scale quickly with complexity, compliance scope, and integrations. Here’s a realistic snapshot for 2026:
- Basic MVP (e.g., patient-facing mobile app): $90,000–$180,000
- Mid-size system (e.g., custom EHR or RPM platform): $300,000–$650,000
- Enterprise platform (e.g., EHR + telemedicine + integrations): $900,000–$2.5M+
These estimates typically include product design, core development, testing, security, and initial compliance work for the first year. Advanced capabilities—such as AI-driven diagnostics, real-time data processing, or deep third-party integrations—can increase costs significantly.
Ongoing maintenance, security updates, and compliance support usually cost 15–30% of the initial build per year. In healthcare, cutting corners here is rarely cheaper in the long run.
Choosing the Right Medical Software Development Partner (2026)
Your development partner will directly influence quality, compliance, and long-term success. These are the criteria that matter most in 2026:
Proven Healthcare Experience
Medical software has unique clinical and operational constraints. Choose a team with hands-on experience in healthcare projects. Real-world references from providers or health organizations are a strong signal.
Regulatory and Compliance Expertise
Your partner must understand healthcare regulations end-to-end. This includes HIPAA, GDPR, and regional standards. Ask how compliance is built into their development process, not handled later.
Modern Technical Capabilities
Strong technical depth is essential for scalability and security. Look for experience with cloud platforms, APIs, mobile development, and AI where relevant. A modern, well-supported tech stack is non-negotiable.
Transparent Communication
Reliable partners communicate clearly and consistently. Expect regular updates, realistic timelines, and clear documentation. Transparency reduces risk and prevents surprises.
Long-Term Support and Maintenance
Healthcare software requires continuous updates and monitoring. Your partner should provide post-launch support, security patches, and compliance updates. In healthcare, delivery is only the starting point.
Key Trends in Medical Software Development for 2026
Healthcare technology continues to evolve quickly. In 2026, these trends are actively shaping how modern medical software is designed, built, and deployed.
AI and Machine Learning Everywhere
AI is embedded across diagnostics, imaging, and administrative workflows. Risk prediction, automation, and decision support are now standard capabilities. Explainability and accuracy matter more than raw automation.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud infrastructure has become the default for new healthcare software. It enables scalability, resilience, and faster compliance updates. On-premise systems are increasingly limited to legacy environments.
Interoperability Standards
FHIR and HL7 are now baseline requirements, not optional integrations. Systems are expected to exchange data seamlessly across providers. Interoperability directly impacts care coordination and efficiency.
Wearable and IoT Integration
Connected devices continuously stream patient health data. Medical software now supports real-time monitoring and alerts. Chronic care and preventive health are key use cases.
Patient-Centered Product Design
Healthcare software is expected to feel intuitive and accessible. Mobile-first experiences and clear data transparency build patient trust. Usability is a competitive advantage in 2026.
How to Build a Medical Software MVP in 2026
Launching a full platform on day one increases risk and cost. In 2026, successful healthcare products start with a focused MVP designed to validate real demand.
Define One Core Problem
Start with a single, clearly defined use case. This could be appointment scheduling, remote monitoring, or clinical documentation. Solving one problem well creates a strong foundation.
Validate with Real Users
Test early concepts with clinicians, administrators, or patients. Their feedback reveals usability gaps and workflow issues. Real-world input matters more than assumptions.
Build Essential Features
Limit the MVP to features required to deliver value. Each extra feature increases development and compliance overhead. Iteration should be driven by usage data, not guesses.
Plan for Compliance from Day One
Security and compliance are not optional, even for MVPs. Build privacy, access controls, and auditability into the architecture. Early compliance prevents costly rewrites later.
Best Practices for Medical Software Development Teams
Healthcare software demands discipline, coordination, and consistency. High-performing teams follow these practices to reduce risk and deliver reliable products in 2026:
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Successful teams involve developers, clinicians, designers, and compliance experts early. This alignment prevents costly misunderstandings later. Diverse input improves usability and safety.
Agile Development
Agile methods enable faster feedback and controlled iteration. Short sprints and regular reviews keep teams aligned with real needs. Flexibility is essential in regulated environments.
Continuous Testing and Validation
Testing starts early and never stops. Automated tests ensure stability, while manual testing validates real-world workflows. Reliability is non-negotiable in healthcare.
Clear Documentation
Accurate documentation supports development, compliance, and audits. It also simplifies onboarding and long-term maintenance. Poor documentation creates hidden risk.
Proactive Risk Management
Potential technical, regulatory, and usability risks are identified early. Teams track and revisit risks throughout development. Prevention is always cheaper than recovery.
The Real Standard for Medical Software Success
Medical software development is demanding, but its impact is unmatched. When done right, it improves patient outcomes, supports clinicians, and strengthens healthcare systems. Success comes from solving real clinical problems, embedding compliance into every layer, and treating usability as a core requirement not an afterthought.
As you move forward, work with partners who understand healthcare as deeply as they understand technology. In this industry, long-term trust, reliability, and execution matter more than speed.
