Has it ever come to your attention that there’s an element of art in everything humans do? The way one thinks, speaks or be it our point of discussion for today; the way one sells a product. Haven’t we all heard about the art of selling? But it’s not as easy as one might think. Especially, when it comes to selling something like SaaS.
SaaS products over the years have shown impeccable growth. What was market valued at USD 273.55 billion in 2023 is expected to reach USD 317.55 billion in 2024. The role played by SaaS Sales in the same cannot be neglected. Wondering how the sales process takes place? Let’s dive in without further ado!
What Is SaaS Sales?
SaaS (Software as a Service) sales, is the process of selling your business’s web- based software applications hosted in the cloud. The goal of the sales team is to drive recurring revenue by delivering value-added services and continuously improving the software to meet customer needs.
Since the software service is sold in subscriptions rather than one-time purchases, the sales team needs to focus on customer retention and satisfaction to ensure ongoing revenue streams. Also, since SaaS products have a higher level of technical complexity compared to traditional software, the teams need to possess a deep understanding of the software’s features, benefits, and technical requirements to effectively communicate value to customers.
The SaaS Sales Process
The SaaS sales process involves prospecting, educating, and guiding potential customers through subscription-based software. It emphasizes value, customization, and ongoing support to drive conversions, retention, and customer satisfaction.
1. Lead Generation
In the lead generation stage of the SaaS sales process, companies identify potential customers through prospecting methods such as market research, networking, and social media engagement. Outreach efforts involve reaching out to these prospects through personalized emails, cold calls, or targeted advertising campaigns.
Additionally, inbound marketing strategies like content creation, SEO optimization, and social media presence attract leads organically. The goal is to generate a pool of qualified leads interested in the software solution, nurturing them with valuable information and engagement to move them further along the sales funnel.
2. Qualification & Discovery
In the qualification and discovery stage of the SaaS sales process, the primary focus is on identifying and assessing potential customers who are the best fit for the software solution. Sales representatives qualify leads based on predefined criteria such as budget, authority, need, and timeline (BANT).
Lead qualifying involves conducting thorough research and engaging in initial conversations to understand the prospect’s pain points, objectives, and challenges. Additionally, lead scoring points are assigned based on engagement level and fit with ideal customer profiles.
Assessment tools help determine the prospect’s readiness to buy and their likelihood of success with the software. This stage sets the foundation for personalized pitches and ensures that sales efforts are directed towards prospects with the highest potential for conversion and long-term satisfaction.
3. Solution Presentation and Customization
During the solution presentation and customization stage in the SaaS sales process, sales professionals showcase the software’s capabilities through a product demo tailored to the prospect’s needs. They highlight how the solution addresses the prospect’s specific pain points and delivers value.
This stage involves understanding the prospect’s requirements and customizing the demo to showcase relevant features and functionalities. Sales teams emphasize the flexibility of the software and its ability to adapt to the unique workflows of the prospect’s business.
Additionally, the team will address any concerns or objections raised by the prospect, demonstrating how the software can be customized to meet specific requirements. This stage aims to build confidence in the product’s suitability and generate excitement about its potential benefits.
4. Negotiation and Closing
In the negotiation and closing stage of the SaaS sales process, the focus shifts to finalizing pricing, terms, and contracts. Sales professionals collaborate with prospects to address any concerns or objections regarding cost, features, or implementation.
This stage also involves customization to meet specific customer needs, such as scalability or integration requirements. Negotiations may include discussions on subscription tiers, discounts, and payment terms. Once both parties reach an agreement, the sales team facilitates contract finalization, ensuring clarity on terms, conditions, and service-level agreements.
The goal is to secure a mutually beneficial arrangement that satisfies the customer’s needs while maximizing value for the SaaS provider, leading to a successful closure and the beginning of a long-term partnership.
5. Post-sale Support and Onboarding
Post-sale support and onboarding are crucial stages in the SaaS Sales Process. Customer onboarding involves guiding clients through the setup and initial use of the software, ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing value from the start. This includes personalized training sessions, tutorials, and documentation.
Additionally, ongoing customer success efforts focus on maintaining engagement, addressing concerns, and facilitating expansion within the software. Regular check-ins, proactive communication, and access to support resources are key components.
Ultimately, effective post-sale support and onboarding contribute to customer satisfaction, retention, and advocacy, leading to long-term success for both the client and the SaaS provider.
7 Best SaaS Sales Models
1. Subscription-Based Model
The Subscription-Based Model sells software services through recurring subscription payments. Its features include flexible pricing tiers, scalable usage, and regular updates.
Customers benefit from cost-effectiveness, as they pay only for what they use, get access to the latest features without additional costs, and are able to scale up or down their subscriptions as needed.
Significantly, this model fosters long-term relationships with customers, providing predictable revenue streams for the SaaS provider and ensuring ongoing customer engagement.
It aligns with evolving customer preferences for flexible, on-demand software solutions, making it a cornerstone of modern software distribution and business operations.
2. Usage-Based Model
As the name says, the Usage-Based SaaS Sales Model charges customers based on their usage of the software, typically measured by metrics like the number of users, transactions, or data storage.
Its features include flexible pricing where customers pay only for what they use, scalability to accommodate fluctuating usage levels, and transparency in billing. This model offers cost-effectiveness for customers with variable needs, as they avoid paying for unused capacity.
Additionally, it aligns the software’s value with the customer’s actual usage, fostering a mutually beneficial relationship. Usage-Based SaaS encourages adoption and growth, as customers can start small and expand as their usage increases, making it particularly attractive for startups and businesses with unpredictable demand.
3. Freemium Model
The Freemium SaaS Sales Model offers a basic version of the software for free, encouraging users to upgrade to a premium, paid version for additional features or functionality. Key features include a free tier with limited capabilities, allowing users to experience the software’s core functionality at no cost.
When upgraded, the premium version offers advanced features, enhanced support, and expanded usage limits, enticing users to upgrade for greater value. Freemium models rely on the “land and expand” strategy, where users start with the free version and upgrade as their needs grow.
This so-called strategy helps drive user adoption, expands the customer base, and increases revenue through upselling and conversions from free to paid users.
4. Self-Service Model
The Self-Service SaaS Sales Model enables customers to discover, sign up for, and utilize the software independently, typically through a website or app. Key features include a user-friendly interface for easy navigation, transparent pricing plans, and comprehensive documentation for self-help.
Automation tools facilitate seamless onboarding and account management processes, minimizing the need for direct sales involvement. This model empowers customers to evaluate the software at their own pace and convenience, fostering a self-sufficient user experience.
Sales efforts primarily focus on marketing strategies to drive traffic, optimize conversion rates, and encourage user engagement. Additionally, analytics and feedback mechanisms provide insights to continuously improve the product and enhance the overall customer experience.
5. Transactional Sales Model
When considering investing more money in a product, customers are less inclined to do so without some interaction with the company. This hesitation stems from a heightened perception of risk due to the higher price tag.
The Transactional Sales Model eliminates this risk by employing inside sales teams and a variety of online content to establish relationships with potential clients and convert them into sales. By far it is the most common sales model as it is the most scalable.
In this model, the marketing department’s focus shifts to lead generation and nurturing prospects or assisting customers through the purchasing process via content marketing.
6. Enterprise Sales Model
The Enterprise SaaS Sales Model focuses on selling subscription-based software solutions to large organizations. Its features include highly personalized sales engagements tailored to meet the specific needs and requirements of enterprise clients.
Sales teams engage with multiple stakeholders across different departments, conducting in-depth consultations, demonstrations, and negotiations. Customizations and integrations are common to ensure seamless adoption and integration with existing systems.
Enterprise SaaS sales typically involve longer sales cycles and higher deal values, requiring a strategic approach to relationship-building and account management. Continuous support and collaboration with clients post-sale are essential to drive customer success and maximize retention within the enterprise market segment.
7. Trials and Demos
The Trails and Demos involves offering potential customers access to guided trials or demos of the software. During a trial, users can explore the features and functionalities of the product firsthand, typically for a limited time or with restricted access.
Demos, on the other hand, are interactive presentations conducted by sales representatives to showcase the software’s capabilities and address specific customer needs. This model allows prospects to experience the value of the software before making a purchasing decision, helping to increase conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, it enables sales teams to gather feedback, tailor solutions, and nurture leads effectively, ultimately driving revenue growth and long-term success.
Key SaaS Sales Metrics
1. MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue)
MRR is a crucial SaaS sales metric representing the predictable revenue generated from subscription-based services each month. It encompasses all recurring subscription fees from customers. MRR provides insight into revenue trends, growth rates, and the overall health of a SaaS business, guiding strategic decisions and forecasting future revenue streams.

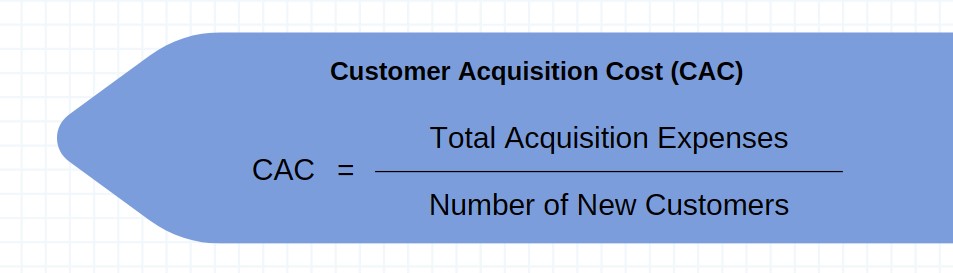
2. CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost)
CAC as a SaaS Sales metric representing the average expense incurred to acquire a new customer. It includes sales and other related costs divided by the number of customers acquired within a specific period. Monitoring CAC helps businesses evaluate the effectiveness of their sales strategies and assess overall profitability.
3. Churn Rate
Churn Rate is a vital metric as it measures the percentage of customers who cancel their subscriptions within a specific period. It indicates customer retention and product satisfaction. High churn rates can signal issues with the product or customer experience, highlighting the need for improvement in sales and retention strategies and customer success efforts.

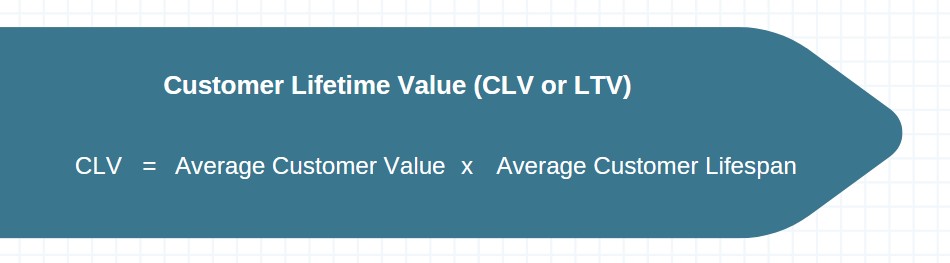
4. CLV (Customer Lifetime Value)
CLTV represents the total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their relationship with the company. It helps assess customer profitability, acquisition and retention strategies, and prioritize resources. Maximizing CLV involves nurturing long-term customer relationships and driving recurring revenue through subscription renewals and expansions.
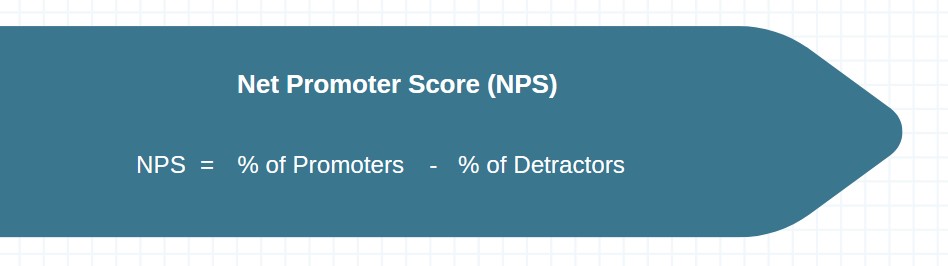
5. NPS (Net Promoter Score)
NPS measures customer loyalty and satisfaction by asking the question: “On a scale of 0-10, how likely are you to recommend our product to a friend or colleague?” Responses categorize customers as Promoters (9-10), Passives (7-8), or Detractors (0-6). NPS indicates overall customer satisfaction and loyalty, critical for growth and retention in SaaS sales.
5 Tips for Successful SaaS Selling
1. Understand Your Customer’s Needs
Understanding customer needs is vital be it in any business, as it enables tailored solutions. By actively listening and empathizing with clients, sales professionals can uncover pain points and goals, positioning their product as the ideal solution.
This approach fosters trust and credibility, increasing the likelihood of conversion and long-term customer satisfaction. Ultimately, aligning the SaaS offering with the specific needs and objectives of the customer enhances the overall sales experience and drives success.
2. Focus On Benefits, Not Features
In SaaS selling, emphasizing benefits over features resonates with customers’ needs and pain points, illustrating how the software solves their problems and improves their operations. This approach fosters a deeper understanding of the software’s value proposition, making it more compelling to potential buyers.
By highlighting the tangible outcomes and advantages that customers will experience, sales teams can effectively drive conversions and build long-term relationships.
3. Provide Value through Education
Providing value through education in SaaS selling involves educating potential customers about the features, benefits, and value proposition of the software solution. By offering informative content, tutorials, webinars, and demos, sales teams empower prospects to make informed decisions.
This approach builds trust, establishes expertise, and helps customers understand how the software addresses their pain points. Additionally, it positions the salesperson as a trusted advisor rather than just a seller, leading to higher conversion rates, customer satisfaction, and long-term loyalty.
Overall, educating customers about the value of the SaaS solution creates a win-win scenario where both parties benefit from a successful partnership.
4. Offer a Seamless Onboarding Experience
Offering a seamless onboarding experience in SaaS selling ensures that customers can easily adopt and integrate the software into their workflow. This includes providing intuitive setup processes, comprehensive training materials, and responsive customer support.
By simplifying the transition for customers, they can quickly realize the value of the software, leading to higher satisfaction, reduced churn, and increased likelihood of future upgrades or expansions.
A smooth onboarding experience also enhances the reputation of the SaaS provider, fostering positive word-of-mouth referrals and driving further growth.
5. Focus On Customer Success
Focusing on customer success ensures that customers derive maximum value from the software. By actively supporting customers throughout their journey, addressing their needs, and helping them achieve their goals, businesses can foster long-term relationships, reduce churn, and drive expansion revenue.
Prioritizing customer success not only enhances satisfaction but also leads to positive referrals, brand advocacy, and sustainable growth in the competitive SaaS market.
Closing Thoughts
SaaS selling represents a dynamic approach to distributing software, offering scalability, flexibility, and recurring revenue opportunities. Understanding the step-by-step sales process, from lead genaration to post-sale support, is essential for success in this competitive landscape.
Moreover, exploring various SaaS sales models allows businesses to tailor their strategies to target markets effectively. Finally, prioritizing customer success emerges as a crucial tip, fostering loyalty, retention, and advocacy.
By embracing these insights, SaaS sellers can navigate the complexities of the industry, drive growth, and unlock the full potential of their software solutions.
😎 Also read some of our other best pieces related to SaaS Sales –
What Is SaaS Marketing? Everything You Need to Know in 2024
20 Best SaaS Tools for Businesses in 2024
10 Best SaaS CRM Software Tools for 2024

